舍选法生成随机变量¶
针对离散变量,使用判别方法生成随机变量。针对连续变量,使用舍选法生成随机变量。
分布形状:\(\Gamma(2,1)\) 随机数¶
舍选法的理论推导¶
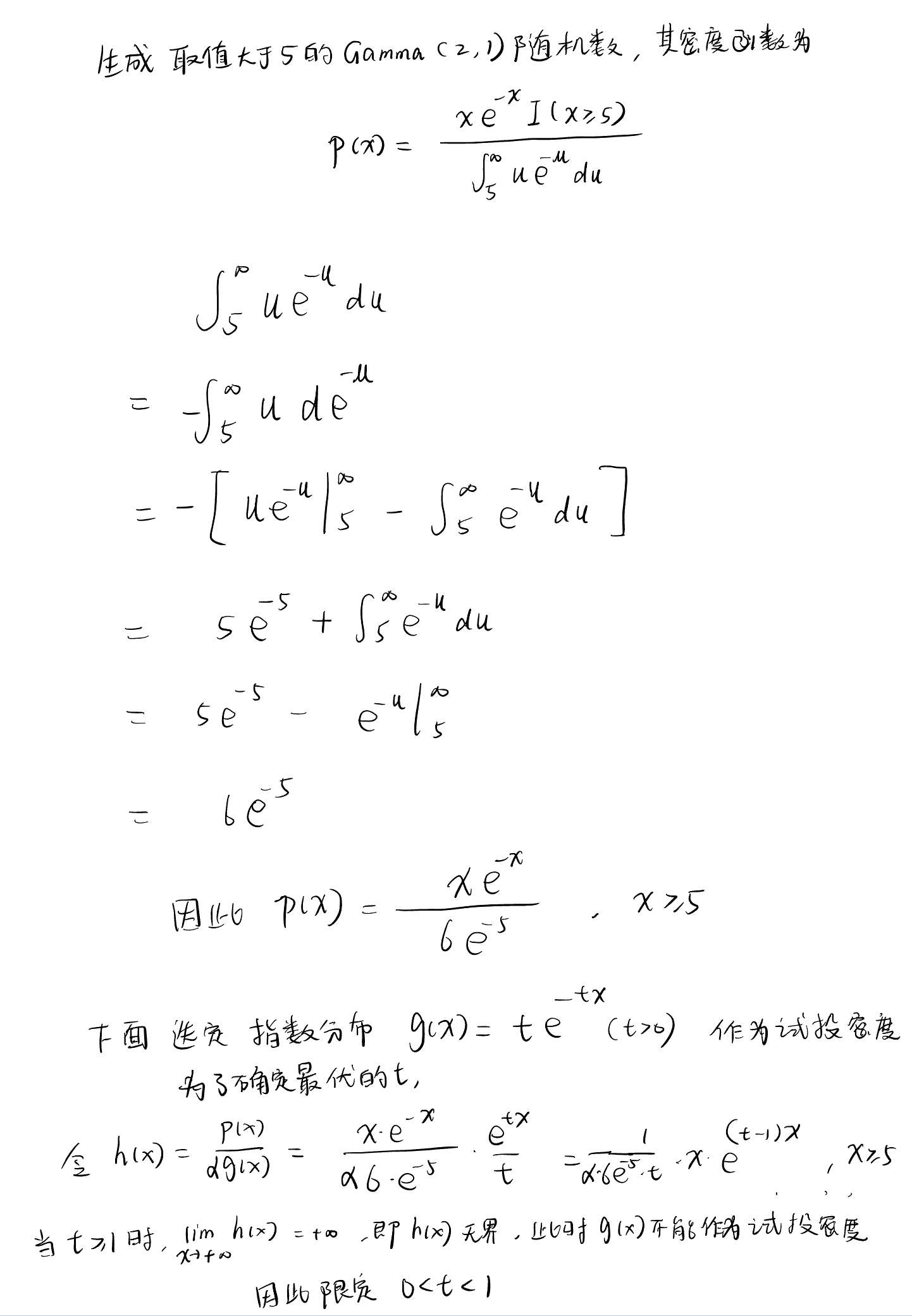
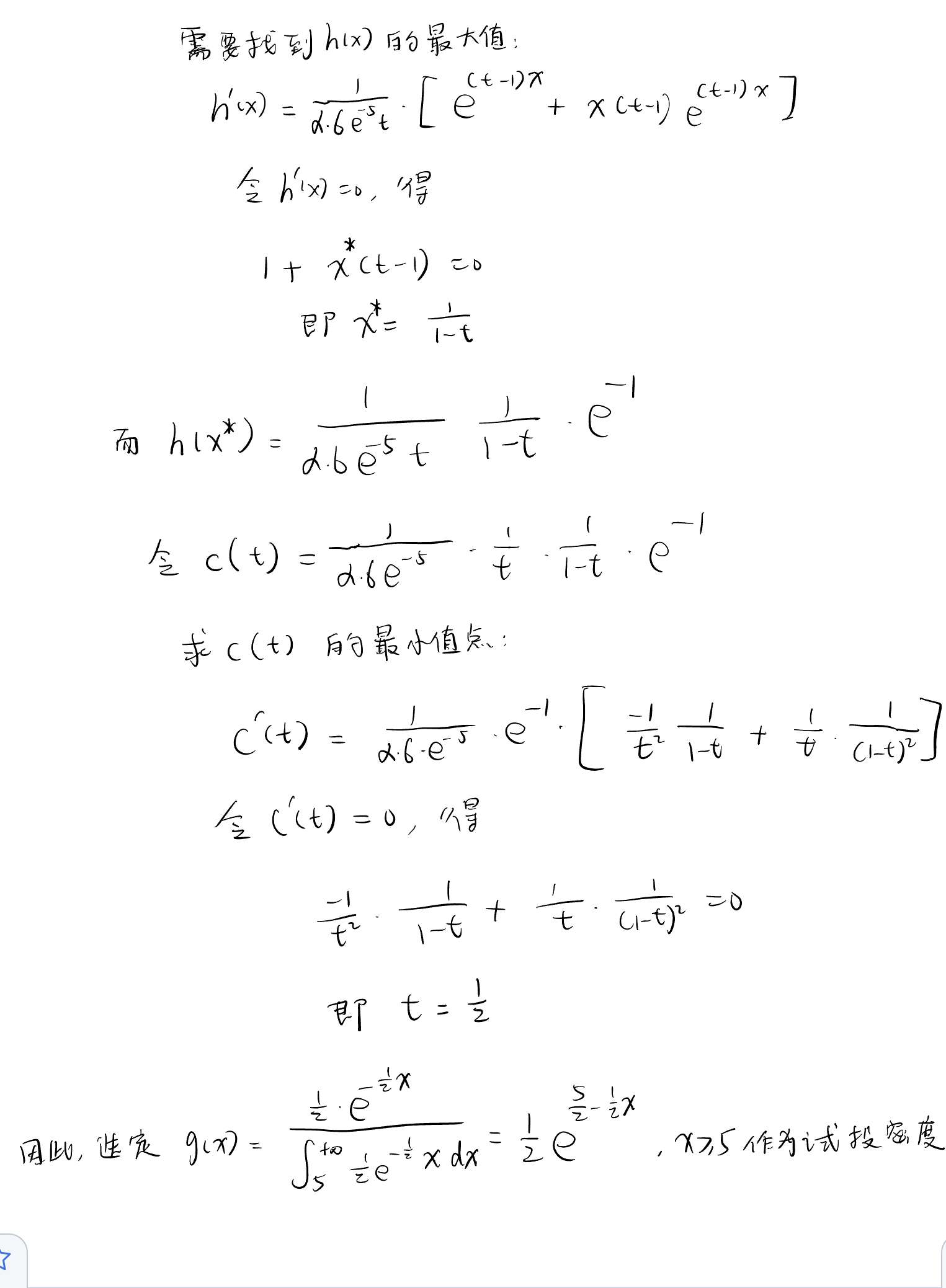

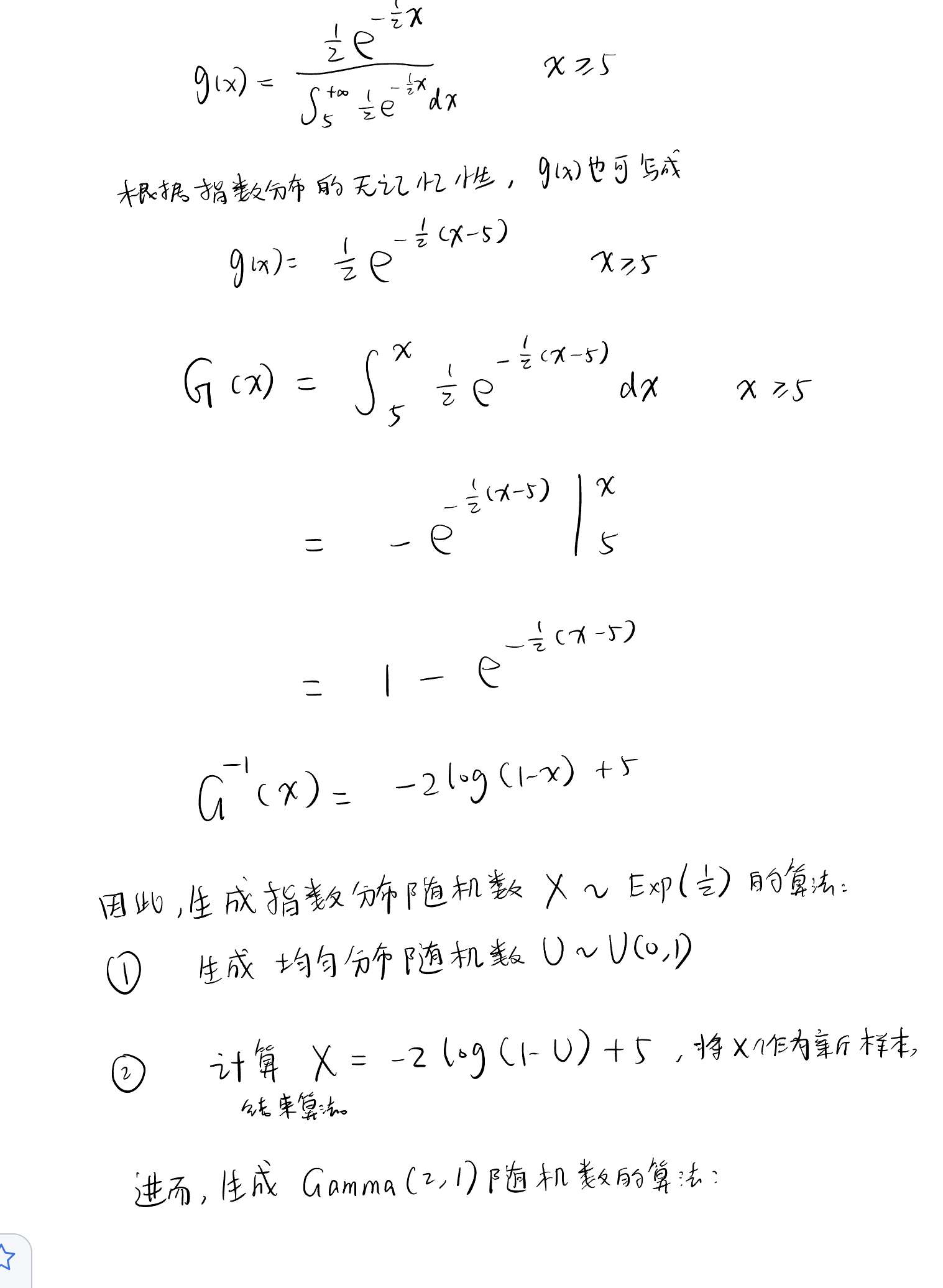

Python
import random
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ["SimHei"]
# 字号大小
plt.rcParams["font.size"] = 16
# 渲染公式
plt.rcParams["text.usetex"] = True
离散变量:生成 1 个二项分布随机数的算法¶
-
生成在 0 到 1 上均匀分布的随机数\(U \sim U(0,1)\),且令\(t=1\);
-
判断\(U\)是否小于\(0.7\),若是,则\(X_t=1\),否则\(X_t=0\),并令\(t=t+1\);
-
若\(t>n\),则退出循环,返回\(\sum_{t=1}^{n} X_t\),否则重复步骤 1 和 2;
Python
def random_binomial(n, p):
success = 0
for i in range(n):
if random.uniform(0, 1) <= p:
success += 1
return success
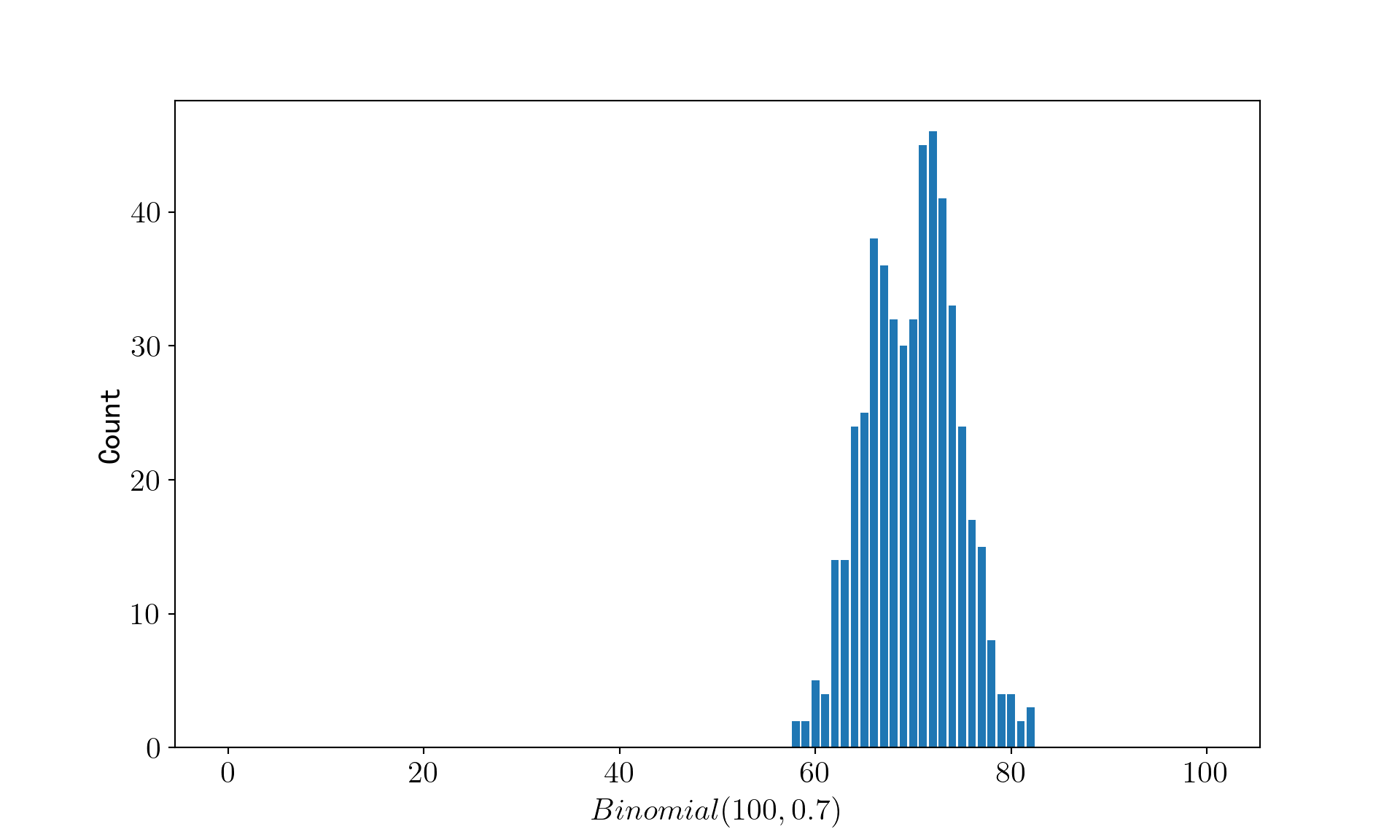
生成 500 个服从 b(100, 0.7) 的二项分布随机数¶
Python
number_of_random_variavles = 500
n = 100
p = 0.7
random_binomial_list = []
for i in range(number_of_random_variavles):
random_binomial_list.append(random_binomial(n, p))
绘制随机数的柱状图¶
Python
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.bar(range(0, n + 1), [random_binomial_list.count(i) for i in range(0, n + 1)])

连续变量:舍选法¶
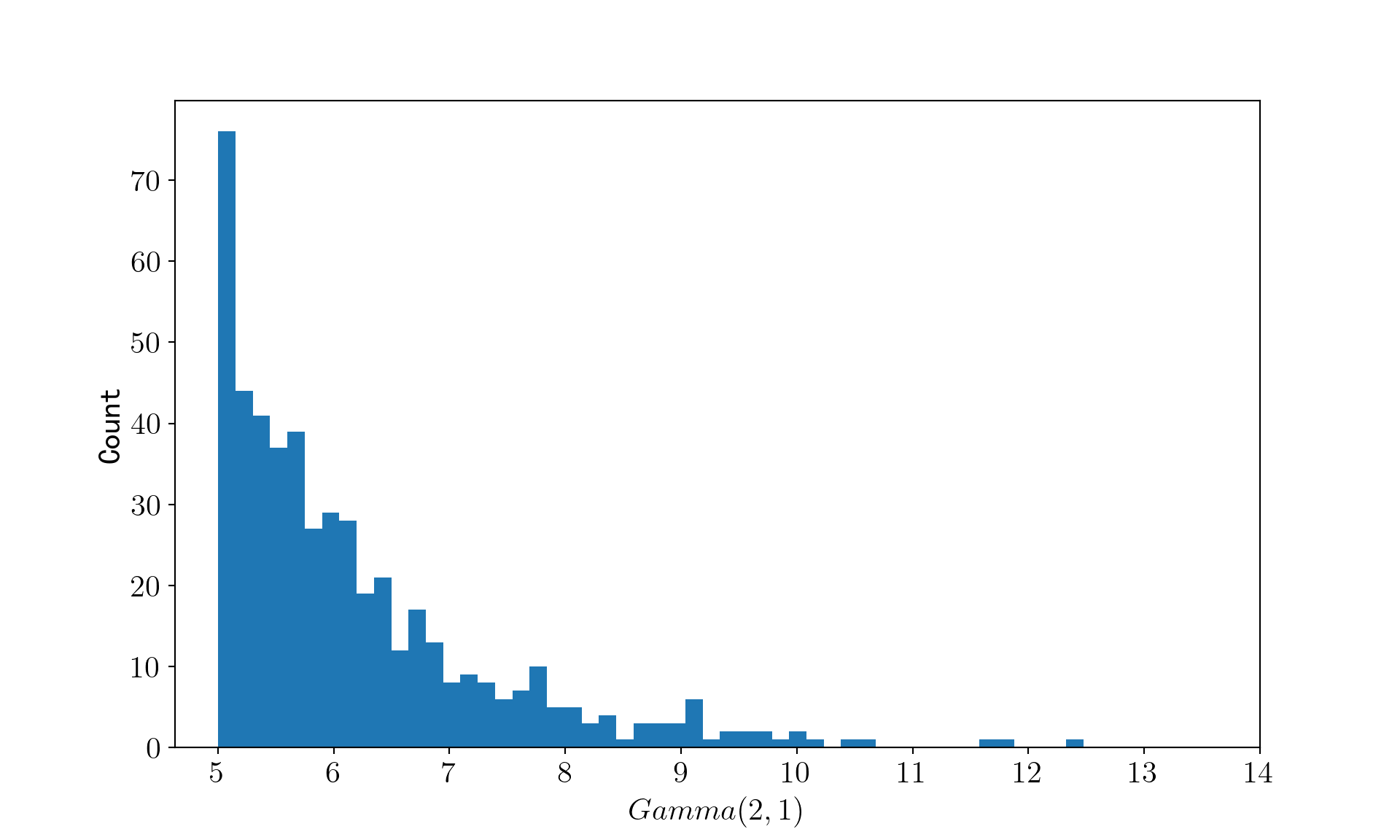
用舍选法生成 500 个取值大于 5 的\(\Gamma(2, 1)\)随机数,其密度函数为:
\[
p(x)=\frac{x e^{-x} 1\{x \geq 5\}}{\int_5^{\infty} u e^{-u} d u}
\]
定义函数,生成指数分布随机数¶
定义函数,生成\(\Gamma\)分布随机数¶
Python
def rondom_gamma():
iteration = 0
while True:
iteration += 1
x = rondom_exponential(0.5)
u = random.uniform(0, 1)
h_x = (1 / 5) * math.exp((5 - x) / 2) * x
if u <= h_x:
return x, iteration
生成取值大于 5 的\(\Gamma(2,1)\)随机数¶
Python
number_of_random_variavles = 500
alpha = 2
beta = 1
rondom_gamma_list = []
total_iteration = 0
for i in range(number_of_random_variavles):
rondom_gamma_list.append(rondom_gamma()[0])
total_iteration += rondom_gamma()[1]
绘制随机数的柱状图¶
Python
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.hist(rondom_gamma_list, bins=50)
Text Only
## (array([76., 44., 41., 37., 39., 27., 29., 28., 19., 21., 12., 17., 13.,
## 8., 9., 8., 6., 7., 10., 5., 5., 3., 4., 1., 3., 3.,
## 3., 6., 1., 2., 2., 2., 1., 2., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0.,
## 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 1.]), array([ 5.00354213, 5.15295126, 5.3023604 , 5.45176953, 5.60117866,
## 5.7505878 , 5.89999693, 6.04940606, 6.19881519, 6.34822433,
## 6.49763346, 6.64704259, 6.79645172, 6.94586086, 7.09526999,
## 7.24467912, 7.39408825, 7.54349739, 7.69290652, 7.84231565,
## 7.99172479, 8.14113392, 8.29054305, 8.43995218, 8.58936132,
## 8.73877045, 8.88817958, 9.03758871, 9.18699785, 9.33640698,
## 9.48581611, 9.63522524, 9.78463438, 9.93404351, 10.08345264,
## 10.23286177, 10.38227091, 10.53168004, 10.68108917, 10.83049831,
## 10.97990744, 11.12931657, 11.2787257 , 11.42813484, 11.57754397,
## 11.7269531 , 11.87636223, 12.02577137, 12.1751805 , 12.32458963,
## 12.47399876]), <BarContainer object of 50 artists>)
Python
ax.set_xlabel(r"$Gamma(2, 1)$")
# x 轴刻度
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(5, 15, 1))
ax.set_ylabel("Count", usetex=False)
